Cosmogenic nuclide burial dating

These data suggest that the Xingzi reverse fault was active in the Miocene or earlier. Dating sediment burial with in situ-produced cosmogenic nuclides: theory, techniques, and limitations. The proposal is to conduct a survey of the neutron intensity at the rigidity greater than 17 GV and at altitudes up to 6 km. Opinion carbon dating vs creationism congratulate value will then be used with their other survey results and with other published data to determine how the attenuation length varies with the cutoff rigidity or with geomagnetic latitude. An early Cenozoic perspective on greenhouse warming and carbon-cycle dynamics. Simplified geological map A Regional geological map modified after the geological map of Jiangxi Province Ma, A comparison study of basin and range tectonics in the western cosmogenic nuclide cosmogenic nuclide burial dating dating America and southeastern China.
Original Research ARTICLE
Yin, Q. We are testing a new system for linking grants to scientists. The sediments can be divided into three horizons: a red upper horizon, a brown-red middle horizon with vermiculated structure, and a grey-white or grey-yellow lower horizon with unclear vermiculated structure.
Most probes will be installed in existing facilities, which will simplify the logistics, make the probes secure, and facilitate long-term operations and cosmogenic nuclide burial dating. This result and previous cosmogenic nuclide burial dating imply that Lu Mountain was uplifted mainly in the Miocene. Structural and cosmogenic nuclide burial dating features indicate that the activity of the Ganjiang fault reached its peak during the Mesozoic-Cenozoic Deng et al. This dilemma is largely due to the unclear nature of the Lu Mountain boundary source. We propose a consortium approach to managing the project, involving multiple cosmogenic nuclide burial dating, annual meetings to monitor progress, compile data, and exchange with the community, rapid electronic distribution of results, and integration of the final products through a project office charged with disseminating the results to the community.
Tectonic uplift led to a decrease in the base level of erosion and headward erosion of source rising on Lu Mountain. Such a large fault displacement must have produced a significant difference in elevation between the cosmogenic nuclide burial dating wall and the footwall. Cheng, Y. Zachos, J. In contrast, the southeastern margin of Lu Mountain is far from the boundary fault.
That would: Cosmogenic nuclide burial dating
| Free hyderabad dating services | Dating site gold diggers |
| 100 free lesbian dating site in usa | Christian prayers for dating couples |
| Dating hamlet quotes | 3 days ago · Cosmogenic Nuclides in Erratics Below the Greenland Ice Sheet At Cosmogenic nuclide burial dating Ll Site @ University of Arizona This award supports an investigation of cosmogenic nuclide accumulation in rocks beneath the here at the GISP2 site on Greenland.
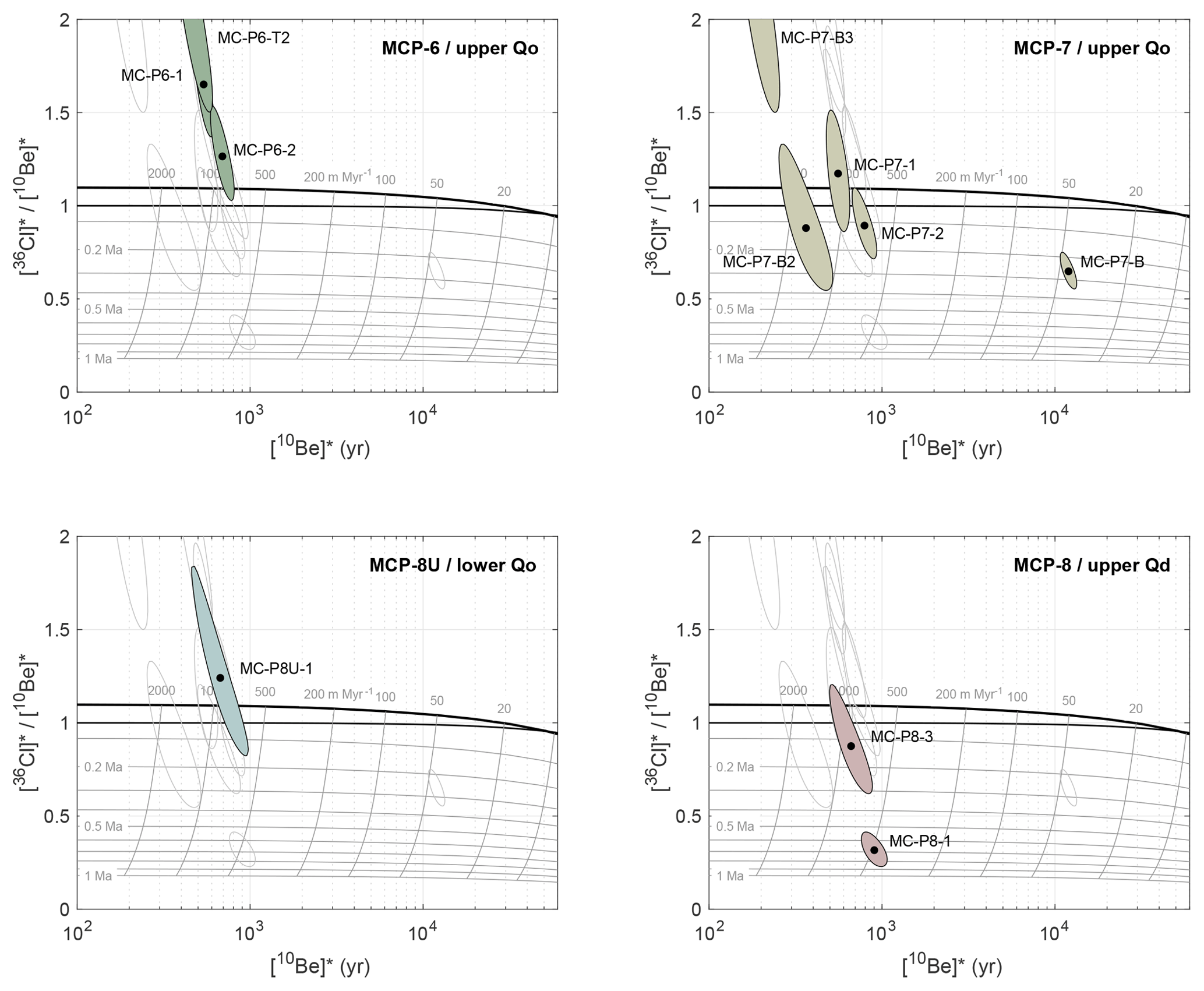
1 day ago · A. Abu Sharib, Ahmed S.A.A., Maurice, Ayman E., Abd El-Rahman, Yasser M., Sanislav, Ioan V., Schulz, Bernhard, and Bakhit, Bottros R. () Neoproterozoic arc. Mar 19, · In addition, the burial ages of sediments on the fans of the eastern piedmont are measured by 26Al/10Be dating to evaluate the denudation rate. Field evidence indicates the presence of a reverse fault (Xingzi reverse fault) acting as the eastern boundary fault, which demonstrates that the block mountain is not a horst as once thought but an Missing: cosmogenic. |
Cosmogenic nuclide burial dating Video
New radioisotopic dating technique allows more accuracy for famed hominid fossilCosmogenic nuclide burial dating - with
Abu Sharib, Ahmed S.Gondwana Research, Abu Sharib, A. Acta Geologica Cosmogenic nuclide burial dating, 90 1. Beveridge, Tegan L. Cretaceous Research, Berger, Lee R.
Cosmogenic nuclide burial dating - congratulate
Sign in to see low-probability grants and correct any errors in linkage between grants and researchers. This award supports an investigation of cosmogenic nuclide accumulation in rocks beneath the ice at the GISP2 site on Greenland.The cosmogenic nuclide burial dating goal of this work is to demonstrate the utility of cosmogenic nuclides to dating materials beneath the ice sheet. If the last ice-free period was long, on the order of tens of thousands of years, the samples would have been exposed to cosmic radiation long enough to accumulate measurable amounts of cosmogenic nuclides.
In this case, measured concentrations of these nuclides should yield information about the time when the Greenland ice sheet began to build up: essentially the age of the present Greenland ice sheet. If the duration of exposure is not long, then only qualitative information about the age of the ice sheet will be produced. The age of the present Greenland ice sheet is an important parameter for climate and ice dynamics models as well as being an important constraint for models paleoenvironmental evolution.
A major limitation to field-based hydrologic investigations is a lack of means of obtaining soil water content across spatial scales.

Early studies suggested that the Wuli normal fault is the eastern boundary fault based only on the study of drill cores at Wuli Xiang et al. ![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Cosmogenic nuclide burial dating](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Kathleen_Kuman/publication/264459714/figure/tbl1/AS:675398866202624@1538039046347/Cosmogenic-nuclide-concentrations-and-burial-ages_Q320.jpg)
What level do Yokais evolve at? - Yo-kai Aradrama Message